Flow Chart
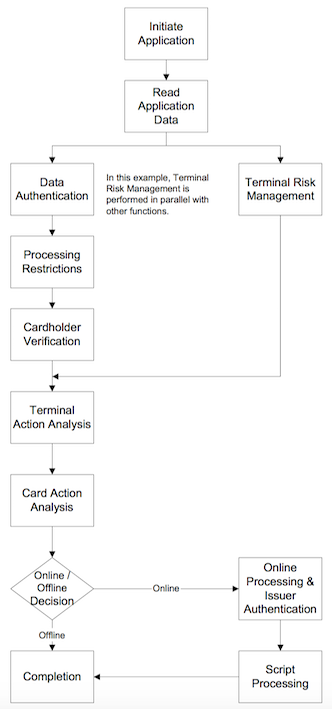
Overall Steps
1.Initiate Application(Select Application)
#Interaction between terminal, smart card and cardholder
#The desired EMV application is chosen(automatically or Manually)
#Application Selection Flag(Canadian Flag)
-Issuer Country Code
-Application Selection Flag --> Priority for ABM or Non ABM
#The chosen EMV Application is activated in both terminal and smart card
#Candidate list: list of EMV application that both terminal and smart card have in common
#Two ways of building a candidate list:
1.PSE -- telephone book store on the smart card
2.Explicit Selection -- AID(RID+PIX+ASI) in terminal
#Built Candidate List with M options
M=number of mutually supported
M=0 -> Terminate transaction
M=1 -> 1.Application may be automatically selected
2.Ask Cardholder confirmation
M>1 -> 1.Sort Application according to their priority
2.Optionally ask cardholder confirmation
?????? ICC has priority list???????? Terminal has priority list ????????????????????????
#The final `SELECT` APDU is issued to the ICC, after the final selection has been made.
@More details in 12.4 EMV 4.2 Book 1
== Explicit Selection ==
#A list of predefined telephone numbers(AID). The terminal tries to select all AIDs in order to determine which applications are present on the smart card.
#Terminal uses `SELECT` APDU to try to select each application(all application) on ICC with all AID
#For each `SELECT`APDU ICC can respond with:
1.`6A 82` File Not Found
2.FCI data ++ `62 89` Application is Blocked
3.`6A 81` Card is Blocked
4.FCI data ++ `90 00` Application Selected
@FCI=File Control Information
@APDU=Application Protocol Data Unit
#If an application is found(SW = `90 00`) compare terminal AID with DF Name in FCI
#Add to candidate list or not
== Candidate List in Terminal ==
AID = RID + PIX + ASI
RID PIX ASI
A0 00 00 03 10 10 Yes
== PSE (Payment System Environment) ==
#PSE is optinal by both ICC and terminal application
#PSE is a directory-like structure on ICC with info about supported application
#Terminal send `SELECT` APDU to ICC with AID=`1PAY.SYS.DDF01`
#ICC can respond with:
1.`6A 82` File Not Found
2.FCI data ++ `62 82` Application is Blocked
3.`6A 81` Card is Blocked
4.FCI data ++ `90 00` Application Selected
@The FCI of the PSE contains the filename SFI of the telephone book
#If it succeed(SW = `90 00`), terminal sends `READ RECORD` APDU indicating the correct SFI(file name of the telephone book) and starting with record #1.
#Compare terminal AID with DF Name in FCI
#Add to candidate list or not
== Final Selection==
#Once the final selection has been made, the `SELECT` APDU is issued to the ICC
[Terminal] [ICC]
SELECT (application)-->
2.Read Application Data(ICC Data)
#The terminal application reads application related information stored in the smart card
#The following APDU's are used:
1.`GET PROCESSING OPTIONS` or GPO -- issued once
2.`READ RECORD` -- issued more than once
@GPO is initial application
@GPO is used to convey PDOL data to ICC, and to retrieve AIP and AFL
@In most cases PDOL is empty PDOL(Processing Data Object List)
#Main Steps:
[Terminal] [ICC]
Step1 SELECT (application)-->
<-- fci="" ++="" `90="" 00`="" -------------="" initiate="" application(select="" application)="" finished="" ---------="" step2="" gpo="" --="">
<-- aip="" ++="" afl="" `90="" 00`="" read="" record="" --="">
<-- record="" data="" read="" --="">
== Record Data Format== (READ RECORD or Record Data)
SFI(first 5 bits) + First Record + Last Record + Num data for offline data authentication
== AIP (Application Interchange Profile) ==
#It indicates which feature are supported by the chip (SDA, DDA CDA, Issuer Authentication)
== AFL (Application File Locator) ==
#It is the index to the subsequent `READ RECORD` APDU's
#It consists of group of 4 bytes, each group indicating a range of records.
3.Data Authentication (Result stored in TVR) indicated in AIP (get from step.2)
#Usig the data retrieved in Step 2, the terminal is able to determine (1)verify the issuer public key(in ICC) by CA public key, and (2)whether the smart card is genuine or not and determine chip authenticity by issuer public key.
#Done by RSA cryptography --> Terminals contains a set of CA public keys: Visa, Master, Interac
#Three methods, depending on chip and terminal capabilities:
1.SDA (Static Data Authentication)
2.DDA (Dynamic Data Authentication)
*3.CDA (Combined DDA/Generate AC) -- Affect card risk management
== CA (Certification Authority) public key == where is CA public keys stored????
#The CA public key is used to verify the issuer public key certificate(Stored on chip). If it is ok, the terminal can trust the issuer public key
#CA public keys are stored in the EMV terminal per RID(first 5 bits of AID)
AID = RID + PIX + ASI
RID PIX ASI
A0 00 00 03 10 10 Yes
#Key ring = RID of application
#Key number = CA public key index
== SDA ==
#SDA is static -- the signature that is verified is the same for every transaction
#SDA consists of 3 steps:
1.Retrieval of CA public key
2.CA public key verify the Issuer Public Key Certificate
3.Issuer public key verify the signed static data (SHA-1 hash)
@Signed static application data is a concatenation of (1)Records indicated in the AFL, and
(2)Data elements in the (optional) SDA Tag list
== DDA ==
#DDA is dynamic -- the signature that is verified is different for every transaction
#For DDA, the chip contains it's own RSA key pair and needs to be RSA-capable
#DDA consists of 3 steps:
1.Retrieval of CA public key
2.CA public key verify the Issuer public key certificate(in ICC) (same as SDA)
3.Issuer public key verify ICC public key certificate
4.ICC public key verify the signed dynamic data (SHA-1 hash)
@ICC private key is used by ICC to generate the signed dynamic data
@Signed dynamic data is generated by 'INTERNAL AUTHENTICATE' APDU
[Terminal] [ICC]
INTERNAL AUTHENTICATE + (DDOL) -->
<--signature over="" data(signed="" dynamic="" data)="="> DDOL(Dynamic Object List) contains data elements that the chip should sign
== CDA ==
#Combine DDA / Generate AC (CDA) is used to prevent fraud by modifying chip communication between ICC and Terminal
#DDA consists of 3 steps:
1.Retrieval of CA public key
2.CA public key verify the Issuer public key certificate(in ICC) (same as SDA)
3.Issuer public key verify ICC public key certificate (same as DDA)
*Step 4 is in Card Risk Management
*4.ICC public key verify the returned AC which was signed using ICC private key
*** Difference from DDA is step.4 will be applied in Card Action Analysis
*.The response to 'GENERATE AC' is signed using ICC private key
*.The actual verification of this signed dynamic data takes place in
steps.8(Card action analysis) and step.11(Online/Offline Decision)
4.Processing Restriction(Result stored in TVR)
#Using the data retrieved in Step.2 Read Application Data, the terminal determines if the smart card application can be used with that particular terminal
#The following checks are carriesd out by the terminal:
1.Application Expiry
2.Activation Date
3.Application version of smart card and terminal application
4.Environment(eg. ATM only, domestic only), using the contents of AUC(Application Usage Control)
@Where is AUC from?????? Step.2??????
#No APDU's are used in this Step.4 because it only used the data retrieved from step2
5.Cardholder Verification(Result stored in TVR)
# The cardholder has to authenticate himself through either:
1.Online or Offline PIN
2.Signature
3.No CVM
4.Future methods can be supported (Biometry)
@The method are depends on (1)CVM List in the chip, and (2)Terminal capabilities
== CVM List ==
Amount X + Amount Y + CV Rule 1 + CV Rule 2 .... CV Rule n
00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 42 01 04 03 xx xx
@CV Rule = CVM Code + CVM Condition Code
@What is X and Y?????????
@How to get CVM List from ICC??? by APDU????
@CVM Code
| value | Meaning |
|---|---|
| '00' | Fail CVM Processing |
| '01'/'04' | Plaintext PIN Verification by ICC |
| '02/42' | Enciphered PIN Verification Online |
| '03/43' | Plaintext PIN Verification by ICC and Signature (Paper) |
| '04/44' | Encipher PIN Verification by ICC |
| '05/45' | Enciphered PIN Verification by ICC and Signature (Paper) |
| '1E/5E' | Signature (Paper) Verification |
| 1F | No CVM |
@CVM Condition Code
| Value | Meaning |
|---|---|
| '00' | Always |
| '01' | If unattended cash |
| '02' | If not unattended cash and not manual cash and not purchase with cashback |
| '03' | If terminal supports CVM |
| '04' | If manual cash |
| '05' | If purchase with cashback |
| '06' | If transaction is in the application currency and is over X value |
| '07' | If transaction is in the application currency and is under X value |
| '08' | If transaction is in the application currency and is over Y value |
| '09' | If transaction is in the application currency and is under Y value |
== Signature ==
#If terminal has the ability to print a transaction receipt, this CVM is successful
#No APDU to ICC
== Online PIN Verification ==
#Card holder will be prompted to enter PIN code
#PIN is encrypted in the PINPad and produced PIN block is stored in terminal
#Note: at this point, it is not yet known whether or not the transaction will go online
#What will happen if the PIN is entered but go offline?????????
#Once PIN is entered, this CVM is successful
#No APDU to chip, same as for MSR
== Offline PIN Verification ==
#Before offline PIN Verification is performed, a 'GET DATA' APDU is sent to the chip to retrieve the PIN Try Counter (PTC)
#If Plaintext PIN -- the PIN is sent directly to the chip for verification
#If Enciphered PIN
-- Prior to offline enciphered PIN verification, 'GET CHALLENGE' APDU is used to obtain a random number from the chip
-- The chip needs to contain a RSA key-pair (this can be a dedicated PIN key, or the same key used for DDA/CDA)
6.Terminal Risk Management(Result stored in TVR) (performed when indicated in AIP)
#This step Terminal Risk Management is only performed when indicated in the AIP (from step.2 get application data)
#It is optional for online-only terminal such as ATM.
#It performs following risk management checks:
1.Transaction Floor Limit of Terminal
2.Transaction Random Selection
3.Exception file
7.Terminal Action Analysis(Terminal Decision)
#In this step, the terminal determines a verdict by the following information
1.TVR
2.IR (Intermediate Result)
3.IAC TAC
Result = (TVR & IR) & (IAC | TAC)
@Follows the order:
1st -> IAC Denial + TAC Denial
2nd -> IAC Online + TAC Online
3rd -> IAC Default + TAC Default ==> in Completion step
<1st>
/ \
AAC <2nd>
/ \
TC ARQC
/ \
(judge ARPC)Online Offline<3rd>
/ \ / \
AAC TC AAC TC
@IAC -- Issuer Action Code
@TAC -- Terminal Action Code
== 1st -> IAC Denial + TAC Denial ==
#If Result != '00 00 00 00 00', the terminal will request an AAC from ICC
#If Result == '00 00 00 00 00', the terminal will proceed to 2nd -> IAC Online + TAC Online
== 2nd -> IAC Online + TAC Online ==
#If Result != '00 00 00 00 00', the terminal will request an ARQC from ICC
#If Result == '00 00 00 00 00', the terminal will request a TC from ICC
== 3rd -> IAC Default + TAC Default ==
#It will be performed on Completion step
@AAC (Application Authentication Cryptogram) --> for Offline Decline
@ARQC (Authorization Request Cryptogram) --> for Online Authorization
@TC (Transaction Certificate) --> for Offline Approval
== Generate AC ==
#At the end of this step Terminal Action Analysis, the terminal communicate the verdict to ICC and get the AC by 'GENERATE AC' APDU sent to ICC, in which 'GENERATE AC' is composed of CDOL1 and AC type.
[Terminal] [ICC]
'GENERATE AC' (CDOL1 data + AC type) --->
------------------- Step 8 Starts ------------------
<--- ac="" (application="" cryptogram)="" @ac="" types:="" --=""> '00' AAC (for Offline Decline)
--> '80' ARQC (for Online Authorization)
--> '40' TC (for Offline Approval)
#This AC will be view as a verdict of terminal decision and will be used for next step
8.Card Action Analysis(Card Risk Management) --> by AC
#ICC can only "overrule" the verdict of terminal by its ICC risk management rules and CDOL data
#Based on the functionality of this step, the ICC will only respond with a more restrictive decision, such as:
-- Visa -defined risk parameters: Application Default Action
-- MasterCard-defined risk parameters: Card Issuer Action Codes, CIAC
#If using CDA,
-- The AC (response to terminal's 'GEN. AC') is signed using ICC's private key only in TC or ARQC.
-- The terminal can verify the authenticity of this AC by ICC's public key
#Terminal can NOT verify the contents of the AC
== CDA (Combine DDA and AC) == in Data Authentication
1.Retrieval of CA public key
2.CA public key verify the Issuer public key certificate (same as SDA)
3.Issuer public key verify ICC public key certificate
*Step 4 is in Card Risk Management
*4.ICC public key verify the returned AC which was signed using ICC private key
*** Difference from DDA is "step.4 will be applied in Card Action Analysis"
*.The response to 'GENERATE AC' is signed using ICC private key
*.The actual verification of this signed dynamic data takes place in
steps.8(Card action analysis) and step.11(Online/Offline Decision)
9a.Online Processing & Issuer Authentication (Online only -- ARQC to ARPC)
The steps of this online processing & issuer authentication:
1.The online authorization message is constructed and sent to the issuer of the card.
2.EMV online process of authorization based on the message terminal sent to it
3.Issuer (1)authorizes the transaction, and
(2)calculates ARPC (Authorization Response Cryptogram), and
(3)sends ARPC back to terminal,
in which -- ARPC is used for Issuer Authentication in the Completion Step and
-- ARPC will be verified by ICC's TDES key
-- Issuer Authentication is based on TDES cryptography
-- Every ICC has a unique TDES key
-- TDES will be derived by using MDK, PAN and PAN sequence number
@ARPC -- Authorization Response Cryptogram
@ARQC -- Authorization Request Cryptogram
9b.Script Processing for Issuer (Online only)
#Issuer Script Processing that allow issuer to perform management actions on ICC and it is signed with TDES MAC
#Issuer Script can optionally be encrypted with TDES encryption key(but necessary in ARPC)
#It can be performed following actions either before or after the transaction is completed
1.Resetting/Changing the PIN(online)
2.Blocking ICC
3.Block and UnBlocking an application
4.Modify the Floor limit of ICC
== How Many Keys stored in ICC ==
1.Issuer Public Key
2.ICC public Key
3.ICC private Key
4.TDES key
10.Completion
IF OFFLINE
Shows the Result AAC(Decline) or TC(Approval) get from Terminal Action Analysis and overrule by Card Action Analysis on the Terminal.
IF ONLINE but CANNOT GO ONLINE
== 3rd -> IAC Default + TAC Default ==
#If Result != '00 00 00 00 00', the terminal will request an AAC from ICC
#If Result == '00 00 00 00 00', the terminal will request a TC from ICC
== Generate AC ==
[Terminal] [ICC]
'GENERATE AC' (CDOL2 data + AC type) --->
<--- ac="" (application="" cryptogram)="" @ac="" types:="" --=""> '00' AAC (Decline)
--> '40' TC (Approval)
#If using CDA
-- the response of the chip is signed under ICC private key
-- ICC public key verify the returned AC which was signed using ICC private key
IF ONLINE and GO ONLINE
== ARPC Judgement ==
#The Terminal judges if it is AAC or TC by reading ARPC content.
== Generate AC ==
[Terminal] [ICC]
'GENERATE AC' (CDOL2 data + AC type) --->
<--- ac="" (application="" cryptogram)="" @ac="" types:="" --=""> '00' AAC (Decline)
--> '40' TC (Approval)
#If using CDA
-- the response of the chip is signed under ICC private key
-- ICC public key verify the returned AC which was signed using ICC private key