Understand replication
How is data replicated among nodes?
Cassandra stores replicas on multiple nodes to ensure reliability and fault tolerance. Areplicationstrategy determines the nodes where replicas are placed. The total number of replicas across the cluster is referred to as thereplicationfactor. Areplicationfactor of 1 means that there is only one copy of each row in the cluster. If the node containing the row goes down, the row cannot be retrieved. Areplicationfactor of 2 means two copies of each row, where each copy is on a different node. All replicas are equally important; there is no primary or master replica. As a general rule, thereplicationfactor should not exceed the number of nodes in the cluster. However, you can increase thereplicationfactor and then add the desired number of nodes later.
Tworeplicationstrategies are available:
SimpleStrategy: Use only for a single datacenter and one rack. If you ever intend more than one datacenter, use theNetworkTopologyStrategyNetworkTopologyStrategy: Highly recommended for most deployments because it is much easier to expand to multiple data centers when required by future expansion.
SimpleStrategy
Use only for a single datacenter and one rack.
SimpleStrategyplaces the first replica on a node determined by the partitioner. Additional replicas are placed on the next nodes clockwise in the ring without considering topology (rack or datacenter location).
NetworkTopologyStrategy
UseNetworkTopologyStrategywhen you have (or plan to have) your cluster deployed across multiple data centers. This strategy specifies how many replicas you want in each datacenter.
NetworkTopologyStrategyplaces replicas in the same data center by walking the ring clockwise until reaching the first node in another rack.NetworkTopologyStrategyattempts to place replicas on distinct racks because nodes in the same rack (or similar physical grouping) often fail at the same time due to power, cooling, or network issues.
When deciding how many replicas to configure in each datacenter, the two primary considerations are (1) being able to satisfy reads locally, without incurring cross data-center latency, and (2) failure scenarios. The two most common ways to configure multiple datacenter clusters are:
- Two replicas in each datacenter: This configuration tolerates the failure of a single node per replication group and still allows local reads at a consistency level of
ONE. - Three replicas in each datacenter: This configuration tolerates either the failure of one node per replication group at a strong consistency level of
LOCAL_QUORUMor multiple node failures per datacenter using consistency levelONE.
Asymmetrical replication groupings are also possible. For example, you can have three replicas in one datacenter to serve real-time application requests and use a single replica elsewhere for running analytics.
Replication strategy is defined per keyspace, and is set during keyspace creation.
To set up a keyspace, see creating a keyspace.

How is data replicated between data centers?
NetworkTopologyStrategy: distribute replicas across racks and data centers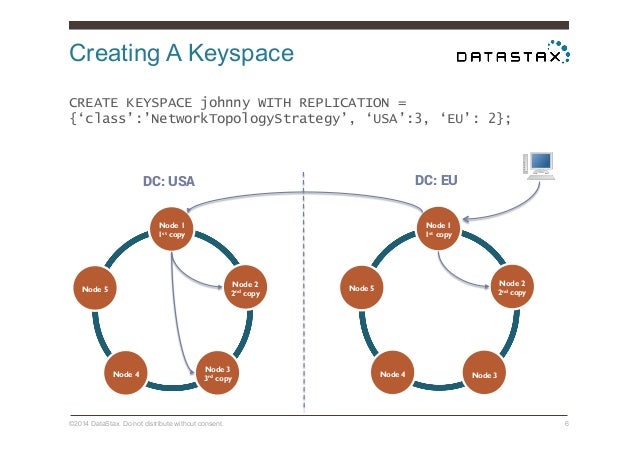
What is a hinted handoff?
A recovery mechanism for writes targeting offline nodes. Coordinator can store a hinted handoff if target node for a write
- is known to be down, or
- fails to acknowledge
Coordinator stores the hint in itssystem.hintstable. The write is replayed when the target node comes online